India’s fiscal landscape is undergoing significant changes, with the government setting ambitious targets for fiscal deficit reduction while grappling with the challenges of economic growth. The fiscal deficit, which represents the gap between the government’s total expenditures and its total revenues, has become a focal point for policymakers and economists alike. As the country aims to balance fiscal prudence with the need for economic stimulation, understanding the implications of a rising fiscal deficit is crucial for future spending strategies.
Understanding Fiscal Deficit
Fiscal deficit occurs when a government’s total expenditures exceed its total revenues, excluding borrowings. This situation necessitates borrowing to bridge the gap, leading to an increase in national debt. The fiscal deficit is expressed as a percentage of the country’s Gross Domestic Product (GDP), providing a clear picture of the government’s financial health.
Importance of Fiscal Deficit
The fiscal deficit is a critical indicator of a country’s economic stability. A high fiscal deficit can raise concerns about financial sustainability, potentially leading to higher interest rates and inflation. Conversely, a manageable fiscal deficit can signal to investors that the government is committed to fiscal discipline, fostering confidence in the economy.
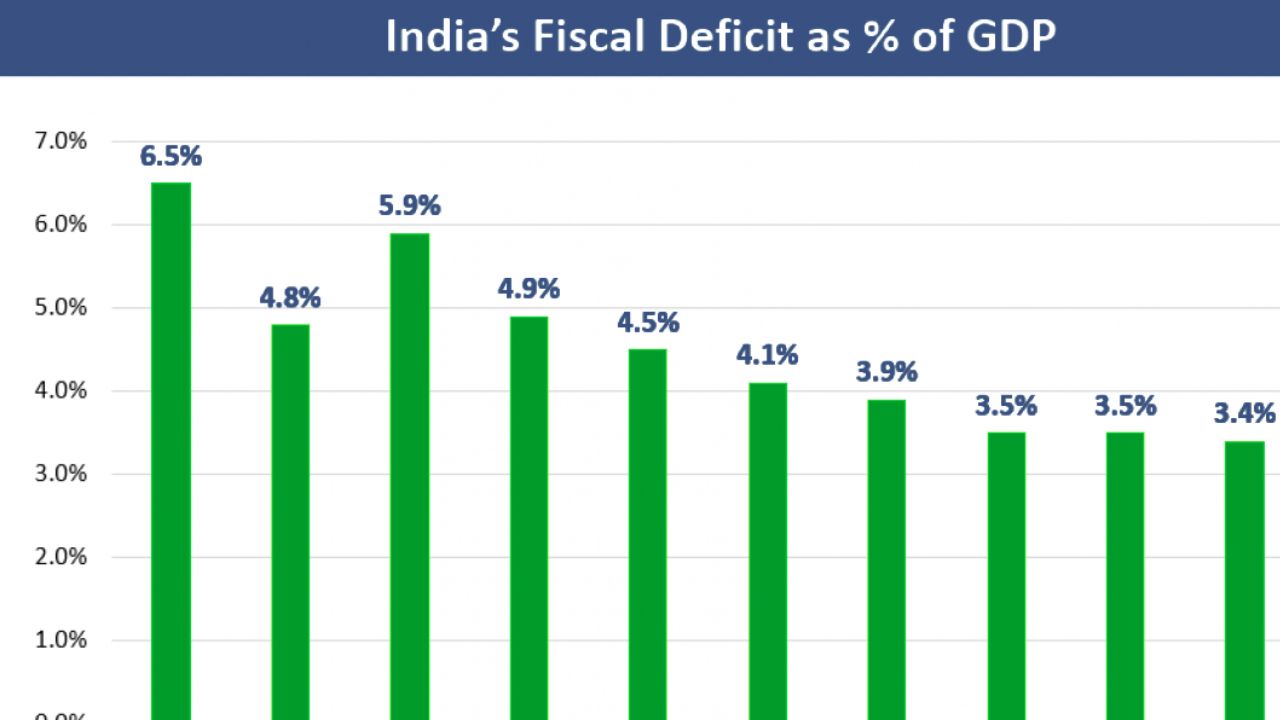
Current Fiscal Deficit Trends in India
As of the latest reports, India’s fiscal deficit is projected to reach 4.4% of GDP for the fiscal year 2025-26, down from 4.8% for the current fiscal year. This reduction reflects the government’s commitment to fiscal consolidation while navigating the complexities of a slowing economy. The fiscal deficit has been a topic of intense discussion, especially in light of the challenges posed by global economic uncertainties and domestic demand fluctuations.
The Government’s Fiscal Strategy
The Indian government, led by Finance Minister Nirmala Sitharaman, has outlined a fiscal strategy that aims to balance growth and fiscal prudence. The strategy includes a shift from a fiscal deficit-based approach to a debt-to-GDP ratio target, which is expected to provide a more sustainable framework for fiscal management.
Key Components of the Fiscal Strategy
- Debt-to-GDP Ratio Target: The government aims to reduce the debt-to-GDP ratio from 57.1% in FY25 to 50% by FY31. This shift reflects a broader understanding of fiscal health, moving beyond mere deficit figures to encompass overall debt management.
- Capital Expenditure Focus: Increased capital expenditure is seen as a catalyst for growth. The government plans to invest in infrastructure, technology, and manufacturing to stimulate economic activity and create jobs.
- Revenue Mobilization: Enhancing revenue collection through tax reforms and improved compliance is a priority. The government aims to simplify tax laws and broaden the tax base to increase overall revenue.
Implications for Future Spending
The government’s fiscal strategy has significant implications for future spending. By prioritizing capital expenditure and revenue mobilization, the government aims to create a conducive environment for economic growth while maintaining fiscal discipline.
The Impact of Fiscal Deficit on Economic Growth
The relationship between fiscal deficit and economic growth is complex. While a high fiscal deficit can hinder growth by increasing borrowing costs, strategic spending can stimulate economic activity.
Short-Term vs. Long-Term Effects
In the short term, a rising fiscal deficit may lead to increased government spending, which can boost demand and support economic recovery. However, in the long term, persistent deficits can lead to higher interest rates, crowding out private investment and stifling growth.
The Role of Capital Expenditure
Capital expenditure plays a crucial role in driving economic growth. Investments in infrastructure, education, and technology can enhance productivity and create jobs. The government’s commitment to increasing capital expenditure is essential for sustaining growth in the face of rising fiscal deficits.
Challenges in Managing Fiscal Deficit
Despite the government’s efforts to manage the fiscal deficit, several challenges remain. These challenges can impact the effectiveness of fiscal policies and the overall economic landscape.
Economic Slowdown
India’s economy has experienced a slowdown, with GDP growth rates declining in recent quarters. Factors such as weak domestic demand, unseasonal rainfall, and global uncertainties have contributed to this slowdown. The government must navigate these challenges while adhering to fiscal targets.
Balancing Growth and Fiscal Discipline
The government faces the difficult task of balancing the need for economic growth with the imperative of fiscal discipline. Critics argue that excessive fiscal restraint may hinder recovery efforts, particularly in sectors reliant on government spending.
External Pressures
Global economic conditions, including rising interest rates and inflationary pressures, can impact India’s fiscal situation. The government must remain vigilant in managing these external factors while pursuing its fiscal objectives.
Investor Sentiment and Fiscal Deficit
Investor sentiment is closely tied to the fiscal deficit. A manageable fiscal deficit can enhance investor confidence, while a rising deficit may raise concerns about the government’s financial health.
Bond Market Reactions
High fiscal deficits typically lead to increased borrowing, which can put upward pressure on interest rates. However, the government’s commitment to fiscal discipline may stabilize bond markets and attract foreign investment.
Equity Market Considerations
The impact of fiscal deficit on the equity market is multifaceted. While increased government spending can boost certain sectors, concerns about fiscal sustainability may lead to volatility in stock prices. Investors must remain informed about fiscal policies and their implications for market performance.
Future Outlook for India’s Fiscal Deficit
The future of India’s fiscal deficit will depend on several factors, including government policies, economic conditions, and global trends. As the government strives to achieve its fiscal targets, understanding these dynamics will be crucial for stakeholders.
Economic Growth Projections
The government has set a nominal GDP growth target of 10.5% for the upcoming fiscal year. Achieving this target will require a concerted effort to stimulate demand and enhance productivity across sectors.
Policy Adjustments
The government may need to make policy adjustments to respond to changing economic conditions. This could include revisiting tax policies, increasing capital expenditure, or implementing measures to boost consumer confidence.
Long-Term Fiscal Sustainability
Ensuring long-term fiscal sustainability will require a balanced approach to spending and revenue generation. The government must prioritize investments that yield long-term economic benefits while maintaining fiscal discipline.
Conclusion
India’s rising fiscal deficit signals a complex interplay between the need for economic growth and the imperative of fiscal prudence. As the government navigates this landscape, its strategies will play a pivotal role in shaping the country’s economic future. By prioritizing capital expenditure, enhancing revenue mobilization, and maintaining a focus on fiscal discipline, India can work towards achieving sustainable growth while managing its fiscal challenges.
In summary, the fiscal deficit is not merely a number; it is a reflection of the government’s commitment to balancing growth and stability. As India moves forward, understanding the implications of its fiscal policies will be essential for investors, policymakers, and citizens alike.